
Farm Animal Worm Infestation
July 4, 2023, 3:28 pm
Endoparasites live inside the body of their hosts. Examples of endoparasites are roundworms, tape worms, liver fluke etc.
Farm Animal Worm Infestation
Roundworms (Ascaris)
They are nutrient sucking internal parasites. Fertilized eggs in the female worm are passed out of the host’s faeces into the soil. The eggs are picked up and swallowed when contaminated feed or water is consumed. When eggs reach the stomach, the digestive enzymes dissolve the egg shells and the young larvae emerge.
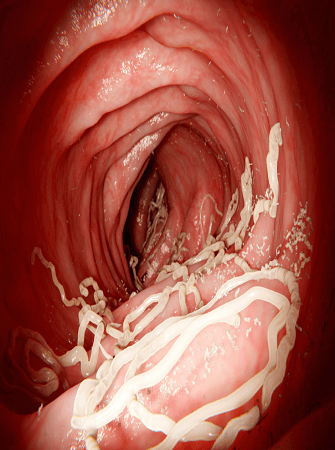
The larvae pierce the intestinal wall and are carried by the blood to the liver, the heart and then to the lungs. In pregnant animals, larvae might cross the placenta and so might affect the foetus. This is why pregnant animals must be free from worms. Lung can be affected and jaundice can result when liver is affected.
When the host coughs, the larva is then swallowed through the gullet into the intestine where it develops into a mature worm or it is vomited. The reproductive cycle then continues.
Tapeworms
These are thorny headed and segmented worms. In most cases, tapeworms are human worms that use pig and cattle as secondary hosts where the larvae spend their lives. Farm animals get tapeworms when they ingest the feed or water contaminated by tapeworm eggs from human faeces.
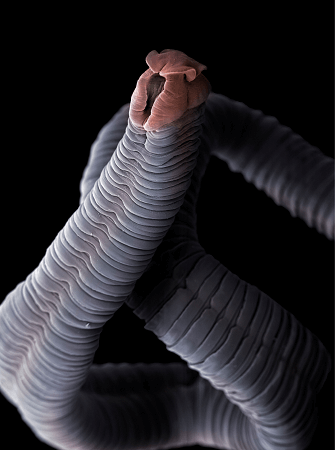
Prevention is by improved sanitation. Taenia solium is generally found in pigs while Taenia saginata is found in cattle.
Difference between Roundworm and Tape Worm
Roundworm is elongated and cylindrical unlike the tapeworm that is long and flat. The body of the roundworm is non-segmented unlike that of the tapeworm. Tapeworm possesses hooks for attachment to the host whereas roundworm does not attach itself to the host. Tapeworm is an hermaphrodite while roundworm is not.
Life Cycle of Tapeworm
A tapeworm possesses both female and male reproductive organs. The tapeworm is therefore an hermaphrodite. The life cycle begins when matured segment called proglottid pulls off the body of the adult tapeworm, it is passed out with the faeces of the host; pig would pick up the eggs while feeding and reaches the pig’s intestine, the embryo is released in the pig’s intestine and it moves to the blood stream through the intestinal wall.
The embryo can then move to the muscles including the heart. A cyst is formed round the embryo with the head turned inside out. This is known as the bladder worm. Raw infested meat should therefore be well cooked or else, enzymes in the stomach would liberate the embryo.
General Signs of Worm Infestation
- Diarrhea
- Rough hair coat
- Loss of appetite
- General unthriftness
- Anaemia
- Loss of weight
- Prevalence of eggs or mature worms in manure when examined under the microscope
- Frequent coughing
General Control Methods of Parasites
- Use of Sulphur drugs called antihelmintics. These drugs can also be fed for control of worms at low levels. The drugs destroy mature worms or attenuate (render non-potent) the worms or make them sterile such that fertile eggs are not produced. Disadvantages are the cost of the drugs and the fact that the parasites might develop tolerance to the drugs
- Use of subcutaneous (under the skin) injection
- Reduction of egg concentration through good sanitation
- Practice rotational grazing
- Manure should be thinly spread and then exposed to sunlight to destroy parasites.
Liver Fluke (Fasciola hepatica)
The water snail is the secondary host of liver fluke while cattle, sheep and goats are the primary hosts. Liver fluke eggs are laid in the bile duct of primary hosts. The eggs are then passed out with faeces. After about ten days, the eggs hatch in water into tiny ciliated larvae called miracidia (singular miracidium). The miracidia swim in water and are attached to water snail change to sporocysts and undergo asexual reproduction, and produce new larvae called redia.
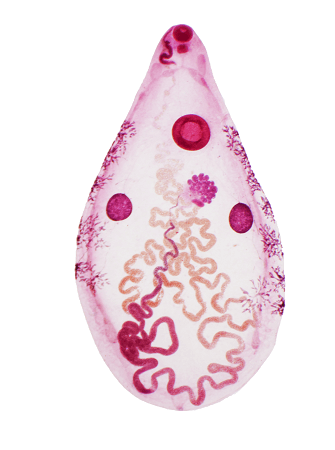
The redia go into the digestive system and develop into minute worms called cercariae which leave the snail and swim to find the primary host which comes around to drink contaminated water. Cercaria could also form cysts on vegetation where they are easily picked up. Cercaria would find their way to the blood stream and to the liver and finally to the bile duct where they develop into adult liver fluke.
Schistosomes
They are flukes. They affect many farm animals including human causing bilharziasis or schistosomiasis. Other endoparasites include coccidian and trypanosome
Helminthiasis
This is a common name given to any of the worm infestation












Share This Article: